Genetic Testing for Muscular Dystrophies - CAM 214
Description
Muscular dystrophies, genetic conditions characterized by progressive muscle atrophy, can be caused by several genetic mutations. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) are due to mutations in the dystrophin gene on the X chromosome (Darras, 2022a). Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) occurs due to a contraction of the polymorphic macrosatellite repeat D4Z4 on chromosome 4q35 (Darras, 2023). The limb-girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMDs) are a group of approximately 30 rare hereditary progressive neuromuscular disorders (Murphy & Straub, 2015) LGMDs result from mutations in genes required for normal muscle function and vary in severity, phenotype, pathology, and age of onset (Darras, 2022b).
Genetic counseling is strongly recommended for individuals pursuing genetic testing for muscular dystrophies.
Terms such as male and female are used when necessary to refer to sex assigned at birth.
Regulatory Status
A search of the FDA Device database on 10/02/2020 for “genotyping tests” yielded 15 results. Additionally, many labs have developed specific tests that they must validate and perform in house. These laboratory-developed tests (LDTs) are regulated by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) as high-complexity tests under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 (CLIA ’88). As an LDT, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has not approved or cleared this test; however, FDA clearance or approval is not currently required for clinical use.
Policy
- For individuals with clinical signs of a dystrophinopathy, genetic testing for likely pathogenic or pathogenic variants of dystrophin (DMD) is considered MEDICALLY NECESSARY.
- For individuals with clinical signs of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD), genetic testing to confirm a diagnosis of FSHD is considered MEDICALLY NECESSARY.
- For individuals who are clinically suspected of having limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD), genetic testing for likely pathogenic or pathogenic variants associated with LGMD is considered MEDICALLY NECESSARY.
- For individuals with clinical signs of congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD), genetic testing to confirm a diagnosis of CMD is considered MEDICALLY NECESSARY.
- For individuals for whom genetic testing was negative for dystrophinopathies, FSHD, LGMD, or CMD, but for whom the clinical suspicion of a muscular dystrophy remains, genetic testing for rare muscular dystrophies (e.g., myotonic dystrophy, Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy, distal muscular dystrophy) is considered MEDICALLY NECESSARY.
- For first- and second-degree relatives (see Note 1) of individuals with a muscular dystrophy, the following genetic testing is considered MEDICALLY NECESSARY:
- Testing restricted to the known familial likely pathogenic or pathogenic variant.
- Comprehensive disorder specific genetic testing when the specific familial likely pathogenic or pathogenic variant is unknown.
The following does not meet coverage criteria due to a lack of available published scientific literature confirming that the test(s) is/are required and beneficial for the diagnosis and treatment of an individual’s illness.
- For all other situations not discussed above, genetic testing for muscular dystrophies is considered NOT MEDICALLY NECESSARY.
NOTES:
Note 1: First-degree relatives include parents, full siblings, and children of the individual. Second-degree relatives include grandparents, aunts, uncles, nieces, nephews, grandchildren, and half-siblings of the individual.
Note 2: For two or more gene tests being run on the same platform, please refer to CAM 235 Reimbursement Policy.
Table of Terminology
| Term |
Definition |
| AAN |
American Academy of Neurology |
| AANEM |
American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine |
| ACMG |
American College of Medical Genetics |
| ALT |
Alanine aminotransferase |
| AMP |
Association for Molecular Pathology |
| ANO5 |
Anoctamin 5 |
| AST |
Aspartate aminotransferase |
| BMD |
Becker Muscular Dystrophy |
| CAPN3 |
Calpain 3 |
| cDNA |
Copy/complementary DNA |
| CGH |
Comparative genomic hybridization |
| CK |
Creatine phosphokinase |
| CLIA ’88 |
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988 |
| CMA |
Chromosomal microarray |
| CMD |
Congenital muscular dystrophy |
| CMS |
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services |
| CNBP |
CCHC-type zinc finger nucleic acid binding protein |
| CNVs |
Copy number variations |
| COL6A1/2/3 |
Collagen type VI alpha [1, 2, or 3] chain |
| CRPPA |
CDP-L-ribitol pyrophosphorylase A |
| CVS |
Chorionic villus sampling |
| DAG1 |
Dystroglycan 1 |
| DCM |
Dilated cardiomyopathy |
| DM1/DM2 |
Myotonic dystrophy |
| DMD |
Duchenne muscular dystrophy |
| DMD |
Dystrophin |
| DMPK |
Dystrophia myotonica protein kinase |
| DNA |
Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DNAJB6 |
DnaJ heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member B6 |
| DNMT3B |
DNA-methyltransferase 3 beta |
| DPPI |
Duchenne Parent Project Italy |
| DUX4 |
Double homeobox protein 4 |
| DYSF |
Dysferlin |
| EDMD |
Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy |
| EMQN |
European Molecular Genetics Quality Network |
| EPNS |
European Paediatric Neurology Society |
| FCMD |
Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy |
| FDA |
Food and Drug Administration |
| FKRP |
Fukutin-related protein |
| FKTN |
Fukutin |
| FSHD |
Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy |
| GMPPB |
GDP-Mannose pyrophosphorylase B |
| HNRNPDL |
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D like protein |
| Hsp40 |
Heat shock protein 40 kD |
| LAMA2 |
Laminin subunit alpha 2 |
| LDTs |
Laboratory-developed tests |
| LGMDs |
Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies |
| LRIF1 |
Ligand-dependent nuclear receptor-interacting factor 1 |
| MDA |
Muscular Dystrophy Association |
| MLPA |
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification |
| mPCR |
Multiplex polymerase chain reaction |
| mRNA |
Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| NGS |
Next-generation sequencing |
| NMDs |
Neuromuscular disorders |
| OMIM |
Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man |
| OPMD |
Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy |
| PABPN1 |
Polyadenosine RNA binding protein, polyadenylate-binding nuclear protein 1 |
| PCR |
Polymerase chain reaction |
| PLEC1 |
Plectin |
| POGLUT1 |
Protein O-glucosyltransferase 1 |
| POMGNT1 |
Protein O-linked mannose N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 1 |
| POMGNT2 |
Protein O-linked mannose N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 |
| POMT1 |
Protein O-mannosyltransferase 1 |
| POMT2 |
Protein O-mannosyltransferase 2 |
| PPMD |
Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy |
| RHDO |
Relative haplotype dosage analysis |
| RNA |
Ribonucleic acid |
| SEPN1 |
Selenon |
| SGCA |
Sarcoglycan alpha |
| SGCB |
Sarcoglycan beta |
| SGCD |
Sarcoglycan delta |
| SGCG |
Sarcoglycan gamma |
| SMCHD1 |
Structural maintenance of chromosomes flexible hinge domain containing 1 |
| SNPs |
Single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| SNVs |
Single nucleotide variants |
| TCAP |
Telethonin |
| TNPO3 |
Transportin 3 |
| TRAPPC11 |
Trafficking protein particle complex 11 |
| TRIM32 |
Tripartite m-containing 32 |
| TTN |
Titin |
| USPSTF |
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force |
| WES |
Whole-exome sequencing |
| ZAK |
Former gene name of MAP3K20 (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 20) |
Rationale
Neuromuscular disorders (NMDs) encompass a diverse set of conditions, many of which arise from specific genetic mutations that impair muscle function and nervous system communication. NMDs are an inherited group of progressive disorders that involve muscle weakness as the primary symptom. Among the most prominent are DMD, BMD, facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) and LGMD. Each disorder has distinct genetic causes and clinical presentations.
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene on the X chromosome, leading to a lack of functional dystrophin, a protein vital for stabilizing muscle fibers. This disorder typically presents in early childhood with muscle weakness, progressive loss of mobility and cardiac or respiratory complications (Darras, 2024a).
Becker muscular dystrophy, similar to DMD, results from mutation in the dystrophin gene but allows for the production of partially functional dystrophin. As a result, symptoms may appear later in life and progress more slowly, often enabling individuals to remain ambulatory into adulthood (Darras, 2024a).
Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy occurs due to the contraction of the D4Z4 repeat region on chromosome 4q35, which leads to the abnormal expression of the DUX4 gene with a protein toxic to muscle cells. Symptoms include weakness in the facial, shoulder and upper arm muscles, with variability in disease severity and progression among individuals (Darras, 2024c).
Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy represents a group of over 30 hereditary disorders characterized by weakness in the muscles around the hips and shoulders. Different genetic mutations affect the proteins required for normal muscle structure and function, resulting in a wide range of severity, onset stages, and disease progression patterns (Darras, 2024d).
In addition to the more well-known forms of muscular dystrophy, several lesser-known types of muscular dystrophy may present clinically. Congenital muscular dystrophies (CMDs) are a heterogeneous group of disorders that present at birth or in early infancy (within the first two years), caused by mutations in genes involved in muscle and connective tissue development. Examples include Walker-Warburg syndrome and Ullrich CMD (Darras, 2024e). Myotonic Dystrophy (DM1 and DM2) occurs as an adult-onset muscular dystrophy characterized by muscle stiffness, weakness, and systemic involvement (such as cardiac issues). This disorder results from mutations in the DMPK or CNBP genes. Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy (EDMD) is caused by mutations in genes encoding nuclear envelope proteins, and leads to early contractures, progressive muscle wasting and cardiomyopathy (Darras, 2024b). Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy (OPMD) is a rare adult-onset dystrophy (mainly autosomal dominant inheritance) associated with mutation in the PABPN1 gene, causing ptosis, difficulty swallowing and proximal muscle weakness (Darras, 2024e). Distal muscular dystrophies are a heterogenous group (over 12 different disorders of myopathies) that affect distal muscles (hands, feet, and forearms) (Darras, 2024e).
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Becker Muscular Dystrophy (BMD)
Dystrophinopathies are due to mutations in the DMD (Dystrophin) gene located on the X chromosome inherited in a recessive pattern. All hemizygous males will exhibit the characteristic phenotype whereas heterozygous females for a pathogenic mutation may exhibit a range of clinical manifestations. If skeletal muscles are affected, dystrophinopathies are classified as either DMD or BMD; however, if cardiac muscle is primarily affected, it is characterized as DMD-associated dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) (Darras, 2024c; Darras et al., 2000).
Duchenne muscular dystrophy, the more severe phenotype of the skeletal muscle dystrophinopathies, typically presents in males before the age of five with progressive, symmetric muscle weakness and calf hypertrophy. Affected males are typically wheelchair-dependent before their teens, and the individual rarely survives beyond their thirties due to respiratory complications and heart failure. BMD is often less severe and manifests later in affected individuals at 30 years of age. Most of these individuals remain ambulatory into adulthood, with some reported to remain ambulatory as late as their sixties. Although skeletal muscle deterioration progresses more slowly in BMD, cardiomyopathy is the most common cause of death in these patients, shortening the life expectancy to the mid-forties. Many BMD patients receive heart transplants within five years after diagnosis of cardiomyopathy (Darras et al., 2000). The prevalence of DMD in the United States has been estimated between 1.3 and 2.1 cases per 10,000 live male births, though the number differed by race/ethnicity in a recent study (Romitti et al., 2015).
Duchenne muscular dystrophy or BMD should be suspected in males with elevated serum creatine phosphokinase (CK) levels (> 10 times of normal and > 5 times of normal, respectively) and clinical symptoms of dystrophinopathy. As permeability of the sarcolemma increases due to muscle damage, creatine phosphokinase is released beyond the normal range, which can be used as a diagnostic value. In DMD, serum CK peaks by age two years, with levels reaching ten to 20 times the upper limit of normal (Darras, 2024a). As the disease progresses, dystrophic muscle fibers begin to decay and the rate of CK release decreases (Kim et al., 2017). Hemizygous female carriers can also exhibit elevated serum CK levels, which are two to ten times that of the normal range. (Darras et al., 2000). A normal CK level, however, makes DMD and BMD unlikely and alternative diagnoses should be considered in these cases.
A variety of genetic testing methodologies are available to assist in the diagnosis of DMD/BMD. In general, it is advisable to try larger deletion/duplication genetic testing first and, if negative, move on to next-generation exome or genome sequence analysis, which can detect "small" mutations [like single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)] as well as micro deletion and duplications (Darras, 2024a). Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) has been used successfully to detect duplication or deletion mutations that cause DMD/BMD. It has also been reported that up to 98% of disease-causing deletions could be detected with multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (Chamberlain et al., 1992). Quantitative PCR, long-range PCR, and chromosomal microarray (CMA) may also be considered; however, CMA is not recommended as a primary confirmatory assay for dystrophinopathies as the sensitivity of the assay may not be sufficient to detect all exon level DMD deletions and duplications (Darras et al., 2000).
Clinical Utility and Validity of DMD/BMD Genetic Testing
A recent Chinese study of 146 at-risk pregnancies in 131 DMD families report a 99% mutation detection rate using “a prenatal diagnosis algorithm for dystrophinopathies that combines multiplex ligation‐dependent probe amplification (MLPA), quantitative PCR, sequencing and linkage analyses” (Wang et al., 2017). This data also shows that 51.1% of the probands had de novo exon deletions. Recombination of the DMD gene occurred in nine of the 146 pregnancies. The authors conclude that “the present results demonstrate the importance of considering maternal germline mosaicism in the genetic assessment. Prenatal diagnosis should be suggested to the parent with a DMD proband whether carrier testing found the causative mutation in the mother's blood or not” (Wang et al., 2017). The reported accuracy rate of this multiplex/quantitative PCR-based method is considerably higher that the reported accuracy rate (>70%) of a real-time PCR assay of the DMD gene (Zhang et al., 2013).
The MLPA-based genetic testing of dystrophinopathies has been reported in many studies with varying degrees of sensitivity. A large study of 1,053 Chinese DMD/BMD patients using MLPA testing reported identifying 70.56% of the probands (Yang et al., 2013) whereas a smaller study of 121 individuals (both male and female) reports confirmation of only 63% of patients and symptomatic females (Luce et al., 2016). A third study of using an algorithm of mPCR and MLPA on 150 male patients reported a 75% confirmation rate (Murugan et al., 2010). Another study using MLPA concluded that “the reading-frame rule held in 90% to 94% of children, which is consistent with reports from other parts of the world. However, testing by MLPA is a limitation, and advanced sequencing methods including analysis of the structure of mutant dystrophin is needed for more-accurate assessments of the genotype-phenotype correlation” (Vengalil et al., 2017).
In a study by Han et al. (2020), 37,268 females of reproductive age were recruited in Hangzhou, China, to identify definite DMD carriers prior to or early in pregnancy. Participants were screened for high CK activity (> 200 U/L), a typical finding in 50% – 70% of asymptomatic heterozygous female DMD carriers (Brandsema & Darras, 2015), and DMD family history. The screening process narrowed down the number of participants for DMD genetic sequencing performed with MLPA to detect gross deletions and duplications and next-generation sequencing (NGS) based on multiplex PCR to detect the small point mutations, insertions, and deletions. From the 37,268 participants, 427 females were identified to have CK levels above 200 U/L and 16 females with a previous family history of DMD. A total of 427 females with high CK levels were asked to repeat CK testing, to which 281 females agreed, and 62 females showed to have sustained elevated serum CK levels. The 16 participants with DMD family history and 62 females with sustained CK levels > 200 U/L were asked to undergo DMD genetic testing. “MLPA and NGS of the DMD gene identified six definite DMD carriers with clear pathogenic variants (3 of the 16 subjects with positive family history and three of the 62 subjects with negative family history). … Four cases had deletions and/or duplications of DMD gene, mostly located in a hotspot mutation region (exons 44 – 55), one case carried a previous reported pathogenic missense variant, and a novel deleterious frameshift pathogenic variant was found in one case” (Han et al., 2020). Results of the screening for DMD carriers are summarized in the figure below (Han et al., 2020).
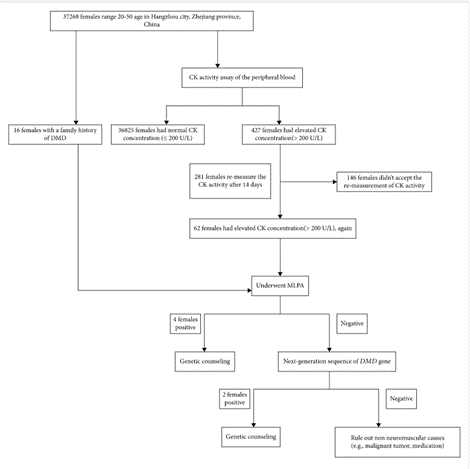
Confirmed carriers of DMD pathogenic variant were provided professional genetic counseling and several reproductive choices such as preimplantation genetic diagnosis, prenatal genetic testing through chorionic villus, amniotic fluid, or umbilical cord blood sampling during different gestation weeks as needed. The authors state that current carrier screening for DMD, which is provided for females with a family history of DMD, misses the many spontaneous cases resulting from unsuspected variants. Therefore, the authors suggest that “Carrier screening before or early in pregnancy will allow carrier females to receive genetic counseling and be informed of fertility choices and recurrent risk. Moreover, carrier screening will help carriers prepare for the possibility of manifesting DMD-related symptoms later on in life. … Furthermore, female relatives of positive carriers should be recommended for genetic testing in order to evaluate their carrier status” (Han et al., 2020).
Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy (FSHD)
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy is the third most common type of muscular dystrophy, with an estimated prevalence of four to 12 per 100,000 population (Darras et al., 2000). It is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder that is caused by a deletion of the macrosatellite repeat regions D4Z4 of the DUX4 gene in the subtelomeric region of chromosome 4q. In healthy individuals, the DUX4 gene is epigenetically silenced in somatic tissues; however, contraction of the D4Z4 repeats allows for inefficient chromatin silencing due to abnormal chromatin structure, resulting in inappropriate somatic expression. Unaffected individuals have a variable number of D4Z4 repeats, ranging from 11 to more than 100, whereas FSHD1 patients have only one to ten repeats on one of the copies of chromosome four. The DUX4 protein is usually only expressed in the germline as a DNA-binding protein with presumed transcription factor activity. Its toxicity in somatic cells is unknown. Two forms of FSHD have been classified: FSHD1, the major form due to a major contraction of the D4Z4 macrosatellite repeat sequences, and FSHD2, a minor form with a normal number of D4Z4 repeats but abnormal D4Z4 chromatin structure. FSHD2 patients have a disease status that cannot be confirmed by using the standard molecular diagnostic testing used in FSHD1 patients (van der Maarel et al., 2011). Further, 85% of patients with FSHD2 have mutations in the SMCHD1 gene on chromosome 18, which encodes for a chromatin modifier believed to be involved in maintaining the D4Z4 chromatin structure (R. J. Lemmers et al., 2012). Pathogenic variants of DNMT3B and LRIF1 genes are less common causes of FSHD2 (Hamanaka et al., 2020; van den Boogaard et al., 2016). Despite the different genetic causes, the phenotypes of FSHD1 and FSHD2 patients are often clinically indistinguishable (de Greef et al., 2010).
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy patients exhibit a progressive muscular dystrophy with variability of affected muscles between patients. Generally, muscles of the face, arms, legs, shoulders, and abdomen can be affected. Serum-based diagnostic testing for FSHD has been elusive. A cross-sectional study by Petek and colleagues, using high-throughput proteomics, shows that the levels of creatine kinase MM and MB isoforms, carbonic anhydrase III, and troponin I type two were elevated at least 1.5-fold in affected individuals and correlated with the severity and state of disease (Petek et al., 2016). Because of the variability of FSHD, genetic testing is still “the preferred diagnostic choice” (R. J. L. F. Lemmers et al., 2012).
Methylation of the D4Z4 regions also plays a role in disease expression and progression (Haynes et al., 2018; Mul et al., 2018; van der Maarel et al., 2011). A study by Mul and colleagues researched the clinical variability of FSHD1 patients for a possible linkage between the severity of disease, the repeat array size of D4Z4, and D4Z4 methylation. Unsurprisingly, unaffected gene carriers had both a higher number of array repeats and higher methylation levels. One interesting result is that the location of the affected body region did show a correlation between disease severity and DNA modification. “The D4Z4 repeat array size and D4Z4 methylation contribute to variability in disease severity and penetrance, but other disease modifying factors must be involved as well, such as polyadenylation of the DUX4 transcript. Polyadenylated DUX4 transcripts are not degraded and lead to the development of FSHD by a toxic gain of function mechanism (Darras, 2023)(Darras, 2024c). The larger effect of the D4Z4 repeat array on facial muscle involvement suggests that these muscles are more sensitive to the influence of the FSHD1 locus itself, whereas leg muscle involvement seems highly dependent on modifying factors” (Mul et al., 2018).
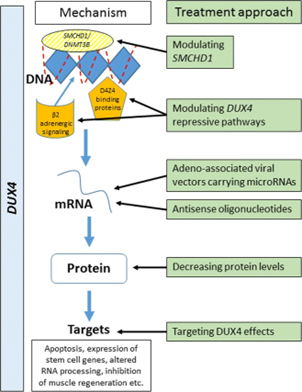
Inappropriate expression of DUX4 in somatic tissue is ultimately responsible for the pathogenesis of FSHD; hence, recent efforts to treat the disorder have targeted the expression of this gene and/or its protein product, as summarized in the table below (Hamel & Tawil, 2018)
Clinical Utility and Validity of FSHD Genetic Testing
The data on the clinical validity and utility of FSHD genetic testing is limited. The American Academy of Neurology and the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine released joint guidelines stating the following: “our systematic review identified nine Class III studies from specialty clinics that, together, demonstrate that the finding of a D4Z4 contraction on chromosome 4q35 likely has a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 98% for diagnosis of clinically defined FSHD” (Tawil et al., 2015). A 2010 study of more than 800 individuals, however, question the criteria for the molecular diagnosis of FSHD. In this study, three percent of asymptomatic, healthy individuals reported a reduced number of D4Z4 repeats, varying four to eight units on chromosome four; further, almost one-half of probands had a normal copy number of D4Z4 repeats. These “results suggest that the genetic basis of FSHD, which is remarkably heterogeneous, should be revisited because this has important implications for genetic counseling and prenatal diagnosis of at-risk families” (Scionti et al., 2012).
The most common method of molecular diagnosis for FSHD is pulsed-field gel electrophoresis with Southern Blotting to discriminate between chromosome four and chromosome ten D4Z4 arrays. A study by Dai and colleagues describes a novel method to characterize the D4Z4 repeat numbers in FSHD by using a single molecule optical mapping platform that helps detect structural variants. With Bionano genome mapping, the number of D4Z4 repeats with 4qA allelic configuration and the levels of postzygotic mosaicism were determined. In the study, the primary cohort consisting of five patients had a confirmed positive diagnosis of FSHD based on Southern blot analysis. The second cohort consisted of eight patients that were suspected to have FSHD, but the patients did not have a prior molecular diagnosis. Optical mapping was performed, and Southern blot was used as a validation assay. In both cohorts, the results obtained from optical mapping have 100% concordance with the results from Southern blot analysis. Although optical mapping is a novel method that can improve accuracy and reliability of FSHD molecular testing, the authors also discuss the disadvantages of the optical mapping platform. Optical mapping is an expensive and time-consuming tool compared to Southern blot, which works reliably for diagnosing patients with one to ten D4Z4 repeats in a cost-effective manner. Despite the disadvantages, the authors believe that costs for optical mapping will decrease and the tool will be incorporated into the clinical setting (Dai et al., 2020).
The genetic diagnosis of FSHD can be confounded by false positive or false negative results. A common test for FSHD uses a p13E-11 DNA probe to confirm a specific deletion that is indicative of the disorder. However, a false negative may occur if the patient has a deletion that affects the diagnostic probe’s region of recognition (Lemmers et al., 2003). A “false” negative result may also occur with this test for patients with FSHD2, since they may not possess the characteristic deletion that is present in typical FSHD1 cases. If clinical suspicion of FSHD exists in patients with a negative test result, then further genetic testing that includes the SMCHD1, DNMT3B, and/or LRIF1 genes may be warranted to confirm FSHD2. Genetic testing should also include haplotype analysis, since a false positive result may occur “if the contracted D4Z4 array is located on the non-permissive 4qB haplotype” (Darras, 2024c).
Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophies (LGMDs)
Together, the group of disorders that constitute LGMD occur with an estimated minimum prevalence between ten and 23 per 100,000 (Wicklund, 2019).The LGMDs vary widely in their genetics and clinical features, ranging from mild forms allowing patients to maintain a fairly normal life to severe deterioration of proximal limb muscles with significant physical weakness and shortened life-span (Monies et al., 2016). A newer definition of LGMD has been proposed as “a genetically inherited condition that primarily affects skeletal muscle leading to progressive, predominantly proximal muscle weakness at presentation caused by a loss of muscle fibres. To be considered a form of limb girdle muscular dystrophy the condition must be described in at least two unrelated families with affected individuals achieving independent walking, must have an elevated serum creatine kinase activity, must demonstrate degenerative changes on muscle imaging over the course of the disease, and have dystrophic changes on muscle histology, ultimately leading to end-stage pathology for the most affected muscles” (Straub et al., 2018).
Approximately 30 LGMDs are recognized currently, most of which are inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. The table below displays the recognized LGMDs according to the updated classification system (Wicklund, 2019):
Nomenclature, genes, and protein products of limb-girdle muscular dystrophies
| NEW nomenclature | Old nomenclature | Gene | Protein |
| LGMD D3 |
LGMD1G |
HNRNPDL |
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D like protein |
| LGMD |
LGMD1I |
CAPN3 |
Calpain 3 |
| LGMD |
|
COL6A1 |
Collagen type VI alpha 1 chain |
| Autosomal recessive |
|||
| LGMD |
LGMD2A |
CAPN3 |
Calpain 3 |
| LGMD |
LGMD2B |
DYSF |
Dysferlin |
| LGMD |
LGMD2D |
SGCA |
Sarcoglycan alpha |
| LGMD |
LGMD2E |
SGCB |
Sarcoglycan beta |
| LGMD |
LGMD2C |
SGCG |
Sarcoglycan gamma |
| LGMD |
LGMD2F |
SGCD |
Sarcoglycan delta |
| LGMD |
LGMD2G |
TCAP |
Telethonin |
| LGMD |
LGMD2H |
TRIM32 |
Tripartite motif-containing 32 |
| LGMD |
LGMD2I |
FKRP |
Fukutin-related protein |
| LGMD |
LGMD2J |
TTN |
Titin |
| LGMD |
LGMD2K |
POMT1 |
Protein O-mannosyltransferase 1 |
| LGMD |
LGMD2L |
ANO5 |
Anoctamin 5 |
| LGMD |
LGMD2M |
FCMD |
Fukutin |
| LGMD |
LGMD2N |
POMT2 |
Protein O-mannosyltransferase 2 |
| LGMD R15 |
LGMD2O |
POMGNT1 |
Protein O-linked mannose N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 1 (beta 1,2–) |
| LGMD |
LGMD2P |
DAG1 |
Dystroglycan 1 |
| LGMD |
LGMD2Q |
PLEC1 |
Plectin |
| LGMD |
LGMD2S |
TRAPPC11 |
Trafficking protein particle complex 11 |
| LGMD |
LGMD2T |
GMPPB |
GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase B |
| LGMD |
LGMD2U |
CRPPA |
CDP-L-ribitol pyrophosphorylase A |
| LGMD |
LGMD2Z |
POGLUT1 |
Protein O-glucosyltransferase 1 |
| LGMD |
|
COL6A1/2/3 |
Collagen type VI alpha 1, 2, or 3 chain |
| LGMD |
|
LAMA2 |
Laminin subunit alpha 2 |
| LGMD R24 |
|
POMGNT2 |
Protein O-linked mannose N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 (beta 1,4–) |
The autosomal recessive LGMD R1 is considered the most common form of LGMD worldwide, making up an estimated 15 to 40 percent of all cases of LGMD (Nallamilli et al., 2018; Wicklund & Kissel, 2014).
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is the most common cardiac phenotype associated with LGMD, and its prevalence varies in the different subgroups of patients. The risk of developing DCM is particularly high in the LGMD1B patient subgroup, such that clinicians might consider preventive interventions due to the high risk of sudden death (Arbustini et al., 2018).
Clinical Utility and Validity of LGMD Genetic Testing
Based on published literature, the clinical validity of genetic testing for LGMD is difficult to ascertain; however, broad genetic testing is becoming the standard for LGMD diagnosis for patients suspected of having LGMD (Wicklund, 2019). Testing should be performed by way of an LGMD or neuromuscular gene panel that looks for alterations in genes known to be involved in LGMD or other dystrophies and myopathies. If such a panel is inconclusive, broader testing by way of whole exomewhole-exome sequencing or whole genome sequence with NGS may be used (Ghaoui et al., 2015; Ozyilmaz et al., 2019). Unless clinical findings suggest a particular subtype of LGMD, whole exomewhole-exome or whole genome testing may increase the likelihood of an accurate diagnosis as compared to single-genesingle gene sequencing (Narayanaswami et al., 2014).
The yield of genetic testing in patients with signs and symptoms of LGMD varies depending on the mutation and population characteristics. Some studies conclude that the clinical validity is reasonably high (Fanin et al., 2009; Norwood et al., 2007). According to Norwood et al. (2007), “DNA analysis directed to provide confirmation of mutation in the affected gene(s) is the gold standard of diagnosis, and necessary to be able to offer carrier or presymptomatic testing to other family members.” Other researchers have attempted to utilize whole-exome sequencing to diagnose LGMD in 100 individuals with familial LGMD; however, a diagnostic success rate of only 45% was achieved (Ghaoui et al., 2015).
Monies et al. (2016) screened 50 random genetically unstudied families with LGMD via a gene panel incorporating 759 OMIM (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man) genes associated with neurological disorders. OMIM is a catalogue of human genes and genetic disorders that provides comprehensive information based on the periodical biomedical literature (Amberger et al., 2014). The panel “identified the mutation in 76% of families (38/50; 11 novel). A total of 34 families had mutations in LGMD-related genes with four others having variants not typically associated with LGMD. The majority of cases had recessive inheritance with homoallelic pathogenic variants (97.4%, 37/38), as expected considering the high rate of consanguinity in the study population.” The authors concluded that the “neurological panel achieved a high clinical sensitivity (76%) and is an effective first-line laboratory test in patients with LGMD and other myopathies. This sensitive, cost-effective, and rapid assay significantly assists clinical practice especially in these phenotypically and genetically heterogeneous disorders. Moreover, the application of the American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) and Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP) guidelines applied in the classification of variant pathogenicity provides a clear interpretation for physicians on the relevance of such findings” (Monies et al., 2016).
Harris et al. (2017) performed whole exomewhole-exome sequencing (WES) on 104 patients with LGMD in which standard gene testing had not yet yielded a diagnosis, and 91 patients using sequential gene by gene testing. They found that “patients selected for WES had undergone more extensive prior testing than those undergoing standard genetic testing, and on average had had eight genes screened already. In this extensively investigated cohort WES identified the genetic diagnosis in 28 families (28/75, 37%), including the identification of the novel gene ZAK and two unpublished genes. WES of a single affected individual with sporadic disease yielded a diagnosis in 13/38 (34%) of cases. In comparison, conventional gene by gene testing provided a genetic diagnosis in 28/84 (33%) families.” The authors concluded that “WES was able to overcome many limitations of standard testing and achieved a higher rate of diagnosis than standard testing even in this cohort of extensively investigated patients. Earlier application of WES is therefore likely to yield an even higher diagnostic rate. We obtained a high diagnosis rate in simplex cases and therefore such individuals should be included in exome or genome sequencing projects. Disease due to somatic mosaicism may be increasingly recognized due to the increased sensitivity of next generation sequencing techniques to detect low level mosaicism” (Harris et al., 2017). A similar study by Reddy and colleagues reported 40% of the LGMD families tested “had novel and previously reported pathogenic mutations, primarily in LGMD genes, and also in genes for Duchenne muscular dystrophy, facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy, congenital myopathy, myofibrillar myopathy, inclusion body myopathy and Pompe disease” (Reddy et al., 2017).
Disease due to somatic mosaicism may be increasingly recognized due to the increased sensitivity of next generation sequencing techniques to detect low level mosaicism” (Harris et al., 2017). A similar study by Reddy and colleagues reported 40% of the LGMD families tested “had novel and previously reported pathogenic mutations, primarily in LGMD genes, and also in genes for Duchenne muscular dystrophy, facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy, congenital myopathy, myofibrillar myopathy, inclusion body myopathy and Pompe disease” (Reddy et al., 2017).
Congenital Muscular Dystrophy (CMD)
Congenital Muscular Dystrophy is a group of genetically diverse disorders that typically manifest at birth or within the first two years of life, marked by muscle weakness, hypotonia, and delayed motor milestones. Initially, CMD was recognized in infants who presented with generalized weakness and abnormal muscle biopsies, revealing fibrosis, fatty tissue infiltration and degeneration of muscle fibers. Arthrogryposis, or joint contractures present at birth, is also common in newborns with CMD (Darras, 2024e).
CMD encompasses both “classic” forms, like merosin-deficient CMD, and more complex “syndromic” forms such as Walker-Warburg syndrome, Fukuyama muscular dystrophy, and muscle-eye-brain disease. Syndromic CMDs often involve structural abnormalities in the brain detected by neuroimaging; these can present with cognitive impairments, developmental delays, and cardiac involvement. Genes associated with CMD in targeted gene panels encompass genes such as LAMA2, COL6A1-3, FKTN, and POMT1-2, among others. Dysfunction can occur across multiple organ symptoms in merosin-deficient CMD (associated with mutations in the LAMA2 gene) (Darras, 2024e).
Clinical Utility and Validity of CMD Genetic Testing
O'Grady et al. (2016) compared targeted next-generation (NGS) panels with traditional candidate gene sequencing in diagnosing CMD. The study included 123 participants with evidence of muscle weakness and hypotonia in the first two years of life. These participants were identified over a 35-year period. Genetic testing targeted key genes, including LAMA2, FKRP, COL6A1-3, and SEPN1. A genetic diagnosis was confirmed for 39 participants (32%), with two additional probable cases. Further NGS using a 45-gene panel, a 336-gene panel, or WES identified causative variants in 11 more individuals, bringing the total diagnostic yield to 59 out of 123 (48%). The study concluded that NGS should serve as the first-line diagnostic tool for CMD, with muscle biopsy reserved for secondary evaluation (O'Grady et al., 2016).
Clinical Utility and Validity of Multi-gene Panel Testing for NMDs
Ebert et al. (2024) drove a retrospective review to analyze the clinical utility and detection rate of genetic testing for individuals with suspected neuromuscular disease. Genetic testing results were gathered for individuals who had received multi-gene panel testing for neuromuscular disorders; the authors analyzed individual records to determine whether the results confirmed or denied a neuromuscular disease diagnosis. A pathogenic mutation or a variant of unknown significance (or both) was found in 77.1% of the study individuals, allowing the confirmation of diagnosis in 35.9%. The most common presenting symptom and indication for testing was suspected neuropathy (53.3%). Myopathy was found in 48.7% of cases. Overall, the authors concluded that the existing evidence constitutes additional confirmatory evidence towards the use of multi-gene panel genetic testing to help the diagnosis and management of neuromuscular disorders. The genetic panel testing was done through Invitae (Ebert et al., 2024).
Rosenberg et al. (2023) investigated the use of multi-gene panel genetic testing to confirm a diagnosis of neuromuscular diseases among 155 patients. They note that clinical evaluation for NMDs has increasingly incorporated molecular genetics as a first or second tier diagnosis practice, especially over the past ten years and that “curated multigene panels of several hundreds of genes remain the most used methodology for the diagnosis of many NMDs. WES is an increasingly popular testing choice when disease presentation is complex and nonclassical.” The authors gathered patient data between 2018 and 2020 using 26 separate genetic tests for a total of 262 individual tests (average of 1.7 tests per patient). Of the patients who had tests performed, over half had a comprehensive NMD panel ordered with between 110 and 211 genes known to be associated with NMDs, inherited myopathies and congenital myasthenic syndrome. The comprehensive NMD panel that was ordered for over half of patients had a diagnostic yield of 14% with 21% of all patients receiving a confirmative diagnosis, which the authors note was low due to the heterogeneity of NMDs and the specific challenge of conditions such as myotonic dystrophy type 1 and facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy, which require specialized molecular testing (Rosenberg et al., 2023).
Best Practice Guidelines on Molecular Diagnostics in Duchenne/Becker Muscular Dystrophies Workshop Report
The international workshop comprised of scientists from Europe, the US, India, and Australia was organized and sponsored by the European Neuro-Muscular Centre, the European Molecular Genetics Quality Network, TREAT-NMD, and Euro-Gentest. The flow chart for the recommended diagnostic work-up of a dystrophinopathy is shown below in Figure 1, located below (Abbs et al., 2010)
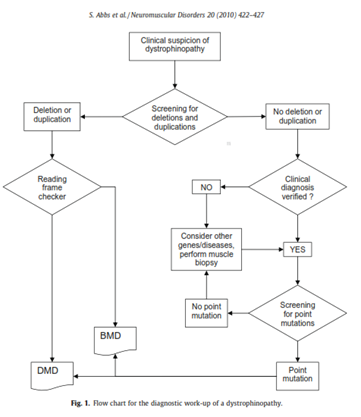
Recommendations for testing are as follows: if there is a clinical suspicion of a dystrophinopathy, first screen for deletions and duplications. Then, if no deletion or duplication is detected, but the clinical diagnosis is verified, screening for point mutations should be performed (Abbs et al., 2010).
The DMD Care Considerations Working Group
The CDC selected 84 clinicians to comprise the DMD Care Considerations Working Group to develop recommendations regarding all aspects of DMD care, including the diagnosis and genetic testing of muscular dystrophy. They state the following: “Testing for a DMD mutation in a blood sample is always necessary even if DMD is first confirmed by the absence of dystrophin protein expression on muscle biopsy. The results of genetic testing provide the clinical information required for genetic counselling, prenatal diagnosis, and consideration for future mutation-specific therapies. ... If analysis by one or more of these techniques leads to the identification and full characterisation of a dystrophin mutation, then no further testing is required. If deletion/ duplication testing is negative, then dystrophin gene sequencing should be done to look for point mutations or small deletions/insertions. Full characterisation of the mutation (deletion endpoints or exact position of any point mutation) is required to allow correlation of the predicted effect of the mutation on the reading frame of the gene, which is the major determinant of the phenotypic variability seen in dystrophinopathy, as well as to determine eligibility for the mutation-specific treatments currently in trials” (Bushby et al., 2010).
An update of the 2010 DMD Care considerations was published to further improve patient care. A diagnostic flow chart for DMD was provided and can be found below (Birnkrant et al., 2018).
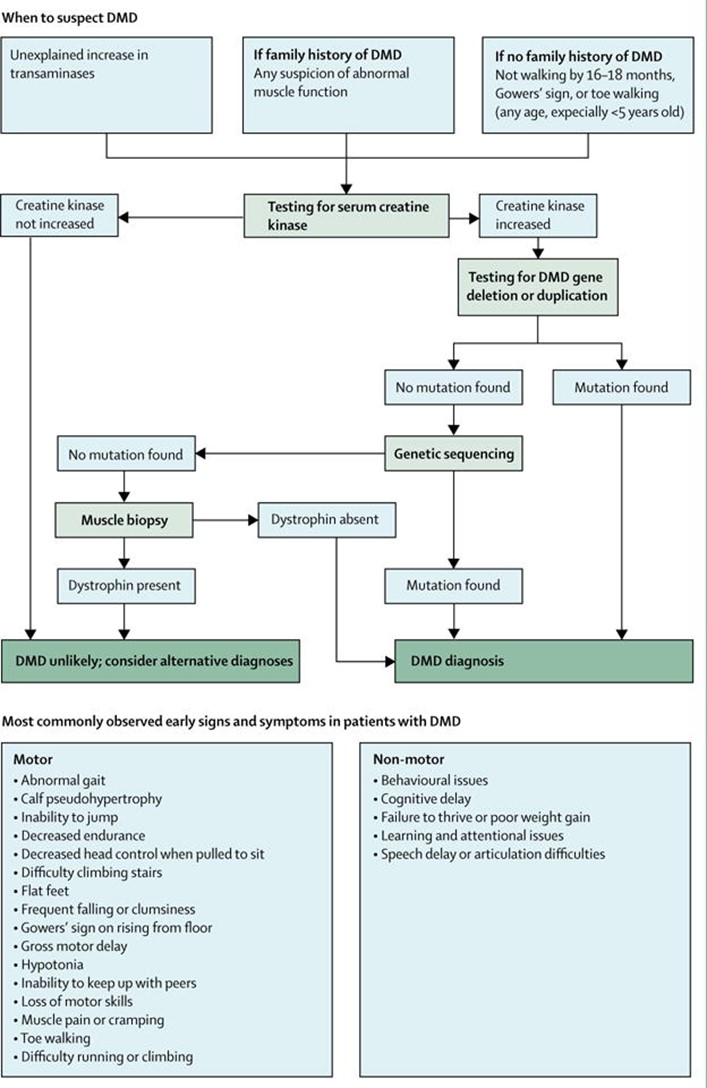
The DMD Care Considerations Working Group has stated that “Because approximately 70% of individuals with DMD have a single-exon or multi-exon deletion or duplication in the dystrophin gene, dystrophin gene deletion and duplication testing is usually the first confirmatory test. Testing is best done by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) or comparative genomic hybridisation array, since use of multiplex PCR can only identify deletions. … If deletion or duplication testing is negative, genetic sequencing should be done to screen for the remaining types of mutations that are attributed to DMD (approximately 25% – 30%). …Finally, if genetic testing does not confirm a clinical diagnosis of DMD, then a muscle biopsy sample should be tested for the presence of dystrophin protein by immunohistochemistry of tissue cryosections or by western blot of a muscle protein extract" (Birnkrant et al., 2018). Also stated is that “Family members of an individual with DMD should receive genetic counselling to establish who is at risk of being a carrier. Carrier testing is recommended for female relatives of a boy or man who has been genetically confirmed to have DMD” (Birnkrant et al., 2018).
American Academy of Neurology (AAN) and the American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM)
The Guideline Development Subcommittee of the AAN and the Practice Issues Review Panel of the AANEM published recommendations that “Targeted genetic testing often identifies causative mutations in the classic CMD subtypes. ... Genetic diagnoses are beneficial to the patient, as they often enable physicians to provide more accurate prognoses and facilitate genetic counseling and family planning discussions, and may enable patients to become more aware of future clinical trials for which they may be eligible… when available and feasible, physicians might order targeted genetic testing for specific CMD subtypes that have well-characterized molecular causes” and “In individuals with CMD who either do not have a mutation identified in one of the commonly associated genes or have a phenotype whose genetic origins have not been well characterized, physicians might order whole-exome or whole-genome sequencing when those technologies become more accessible and affordable for routine clinical use” (Kang et al., 2015).
In 2014, the AAN and the Practices Issues Review Panel of the AANEM issued evidenced-based guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of limb-girdle and distal dystrophies, who made the following recommendations (Narayanaswami et al., 2014) that were reaffirmed in 2022:
For the diagnosis of LGMD:
- For patients with suspected muscular dystrophy, clinicians should use a clinical approach to guide genetic diagnosis based on the clinical phenotype, including the pattern of muscle involvement, inheritance pattern, age at onset and associated manifestations (e.g., early contractures, cardiac or respiratory involvement) (Level B recommendation).
- In patients with suspected muscular dystrophy in whom initial clinically directed genetic testing does not provide a diagnosis, clinicians may obtain genetic consultation or perform parallel sequencing of targeted exomes, whole-exome sequencing, whole genome screening, or next-generation sequencing to identify the genetic abnormality (Level C recommendation).
The AAN Guidelines state: “Diagnosis assists in defining the long-term prognosis, since some dystrophies are more rapidly progressive, involve the cardiorespiratory systems more frequently, or are associated with other disorders. The identification of these dystrophies through genetic testing will not only inform long-term prognosis but will also assist in directing care more efficiently (e.g., more frequent cardiorespiratory monitoring and prophylactic treatments such as pacer/defibrillator placement for those disorders known to be associated with cardiac involvement). Precise identification of the disorder also eliminates the need for repeated testing for an acquired, treatable disorder such as an inflammatory myopathy, because some dystrophies have inflammation on muscle biopsy, making diagnosis difficult on the basis of routine biopsy findings. In addition, the temptation to try immunosuppressive agents repeatedly, looking for a therapeutic response, is not unusual when there is no diagnosis and the patient is worsening. This exposes patients to potentially serious side effects of immunosuppressive medications. Patients on immunosuppressants need regular monitoring, adding logistical difficulties to a population that may have significantly impaired mobility. Health care costs are increased by repeated investigations, immunosuppressive treatments, and laboratory monitoring. Although establishing a genetic diagnosis is expensive on the front end, the costs of continued investigation for other causes and the risks and expenses associated with empiric trials of immunosuppressants make a strong case for establishing a genetic diagnosis, which often provides patients a sense of closure. Establishing a genetic diagnosis is crucial for genetic counseling to inform decision-making about having children and for screening of offspring. Treatment of cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias, and ventilatory failure prolongs life and improves quality of life in patients with other neuromuscular diseases” (Narayanaswami et al., 2014). These guidelines were reaffirmed in 2022.
For the diagnosis of CMD:
“CMDs are often autosomal recessive, but some cases have been found to follow autosomal dominant patterns, by direct inheritance, spontaneous mutations, or mosaicism. The genetic origins of many cases of CMD have been discovered. However, many affected individuals remain without a genetic diagnosis, an indicator that novel disease genes have yet to be identified. Clinical genetic testing is available for virtually all genes known to be associated with CMD.”
Two recommendations regarding CMD diagnosis via genetic testing (reaffirmed 2021):
- “When available and feasible, physicians might order targeted genetic testing for specific CMD subtypes that have well-characterized molecular causes (Level C). Our systematic review indicates that many patients with CMD do not have mutations in one of the currently known genes. The cost of next-generation sequencing (whole-exome and whole-genome sequencing) is dropping rapidly, to the point where these technologies are now readily available to many researchers who seek novel causative disease genes.
- In individuals with CMD who either do not have a mutation identified in one of the commonly associated genes or have a phenotype whose genetic origins have not been well characterized, physicians might order whole-exome or whole genome sequencing when those technologies become more accessible and affordable for routine clinical use (Level C)” (Kang et al., 2015).
American Academy of Neurology (AAN)
The American Academy of Neurology published evidence-based guidelines which found that “the finding of a D4Z4 contraction on chromosome 4q35 likely has a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 98% for diagnosis of clinically defined FSHD.” They recommend that “Clinicians should obtain genetic confirmation of FSHD1 in patients with atypical presentations and no first-degree relatives with genetic confirmation of the disease [Level B].” Concerning the use of genetics as a predictor of severity in FSHD, they recommend, “Large D4Z4 deletion sizes (contracted D4Z4 allele of 10–20 kb) should alert the clinician that the patient is more likely to develop more significant disability and at an earlier age. Patients with large deletions are also more likely to develop symptomatic extramuscular manifestations [Level B]” (AAN, 2018; Tawil et al., 2015). These guidelines were reaffirmed in 2021.
International Standard of Care Committee for Congenital Muscular Dystrophy
As a part of the guidelines concerning newly diagnosed patients, the International Standard of Care Committee for Congenital Muscular Dystrophy recommends that “if a genetic diagnosis is known, the recurrence risk and impact on future family planning should be discussed. Even if the exact genetic defect is not known, recurrence risk can sometimes be discussed using a common genetic model that is often associated with the diagnosis” (Wang et al., 2010).
171st European Neuromuscular Centre International Workshop on Standards of Care and Management of Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy (FSHD)
In a report from the 171st European Neuromuscular Centre International Workshop Standards of Care and Management of FSHD held in January 2010, it is stated that “when a physician concludes facioscapulohumeral syndrome based on clinical findings, the odds are in favor of FSHD, and genetic testing is the preferred diagnostic choice” (R. J. L. F. Lemmers et al., 2012).
Evidence-Based Consensus and Systematic Review on Reducing the Time to Diagnosis of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Joint Report of the EPNS, MDA, PPMD, TREAT-NMD, and DPPI
According to this evidence-based report endorsed by the European Paediatric Neurology Society (EPNS), the Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA), Duchenne Parent Project Italy (DPPI), Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy (PPMD), and TREAT-NMD, “Genetic testing is crucial for obtaining a complete diagnosis of DMD, and should be considered the gold standard” (Aartsma-Rus et al., 2019); accepted DMD symptoms are listed and include “calf hypertrophy (pseudohypertrophy); delayed walking; difficulty climbing/descending stairs; difficulty rising from the floor; difficulty running/walking; elevated serum CK levels (including elevated ALT and AST); a family history of DMD; frequent falls; Gowers' sign; male sex; and muscle weakness;” additional recommendations include that “patients with signs and symptoms of DMD and elevated serum CK levels should be referred for genetic testing to either a clinical geneticist or a neuromuscular specialist” (Aartsma-Rus et al., 2019). Regarding testing of other family members, Aartsma-Rus et al. (2019) recommends that “After a patient receives a complete genetic diagnosis of DMD, it is mandatory that carrier testing of the mother and other at-risk female family members be offered with appropriate pre- and postgenetic counseling.”
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF)
No U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendations for genetic testing for muscular dystrophy have been identified. A search for “muscular dystrophy” on the USPSTF website turned up zero relevant results in October of 2024.
European Molecular Genetics Quality Network (EMQN) Best Practice Guidelines on Molecular Diagnostics in the Duchenne/Becker Muscular Dystrophies
The EMQN summarizes current diagnostic methods to analyze the DMD gene and categorizes these methods according to specificity of the tests into Level one (copy number variations detection), Level two (small variants detection), and Level three (RNA Analysis). Seventy-eight percent of the pathogenic DMD variants is due to whole-exon deletions and duplications; therefore, detection of the relative copy number of all exons within the DMD gene (copy number variations) is the first level of diagnostic tests offered. Several quantitative tests can be used to detect these copy number variations (CNVs). The most reliable method is MLPA, which detects the number of deletions or duplications to the exon level. MLPA is more reliable when there are multiple exons involved, but less if there is a single-exon deletion. Therefore, real-time PCR, multiplex PCR, Sanger sequencing, or microsatellite marker analysis must follow to confirm single-exon deletions. Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) is another method which provides a slightly higher detection rate than MLPA by use of oligonucleotide probes to interrogate copy number across the entire 2.2 Mb genomic region of the DMD gene. The last method is NGS, which can detect single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and CNVs; however, NGS is not routinely used to detect CNVs because it is not sensitive enough to pick up on all types of CNVs. Level two testing detects missense, nonsense, small insertions and deletions, and indel and splicing variants through either Sanger sequencing or NGS. NGS is less time consuming as it allows for many targets to be sequenced with deep sequence coverage in multiple patients at a time and enhances detection of low level somatic mosaicism in patients’ or probands’ mothers; however, Sanger sequencing is still the standard method used for known familial variant testing. Level three testing, such as muscle cDNA analysis, is used when a patient presents with clinical symptoms of a dystrophinopathy, but no CNVs or small variants were detected from Level one and Level two diagnostic techniques.
A flowchart for the recommended molecular diagnostic algorithm for dystrophinopathy is shown in the figure above (Fratter et al., 2020). When dystrophinopathy is suspected due to clinical symptoms, high serum creatine kinase levels, and a possible family history, molecular testing to detect CNVs is recommended. If a pathogenic deletion and duplication is not detected, the next step is to sequence the coding region of the entire DMD gene. If a pathogenic variant is not detected from these two tests, a muscle biopsy, dystrophin gene analysis via immunohistochemistry, or muscle cDNA sequencing may be performed. If the patient presents with a positive muscle biopsy test and positive symptoms of a dystrophinopathy, but no pathogenic variant is detected through genetic testing, the patient should still be diagnosed with a dystrophinopathy (Fratter et al., 2020).
The EMQN also provides guidelines on genetic testing for females affected by dystrophinopathies. Although dystrophinopathies predominantly affect males, females could
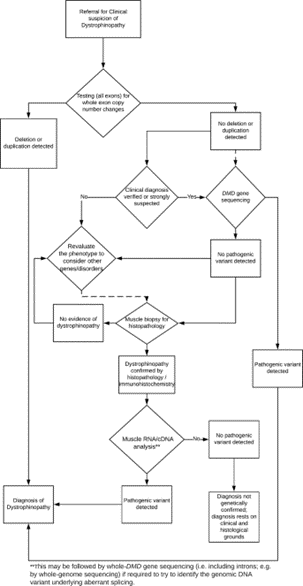
have a pathogenic DMD variant and present with a milder phenotype most likely due to a skewed X-inactivation. In this case, the diagnostic method would be identical to the one presented in the flowchart: evaluation of clinical symptoms, CNV analysis and DMD gene sequencing followed by muscle biopsy, dystrophin gene analysis, and muscle cDNA sequencing as needed. If a female presents with the complete DMD phenotype, karyotyping is recommended due to possible chromosomal aberrations or autosomal translocations that could cause 100% skewed X-inactivation.
Females who are carriers of dystrophinopathies are usually clinically asymptomatic but may develop some symptoms during their lifetime or pass it down to their children. Therefore, carrier testing is important for family planning. If the familial pathogenic variant is known, then two complementary tests should be performed (MLPA and Sanger Sequencing or MLPA and
microsatellite analysis). High density array CGH can also be used, which is a single test that interrogates multiple loci within the deletion or duplication. If the familial pathogenic variant is not known and an affected male in the family is not available, then female carriers who are at risk of being carriers should be offered CNV analysis and DMD gene sequencing followed by muscle biopsy, dystrophin gene analysis, and muscle cDNA sequencing as needed. Measuring serum creatine kinase levels may also be helpful (Fratter et al., 2020).
The EMQN also comments on prenatal diagnosis of dystrophinopathies. Since it is not possible to predict whether a female will present symptoms of a dystrophinopathy, prenatal diagnosis should only be performed on pregnancies with a male fetus unless there is documented familial reoccurrence of complete skewed X-inactivation. Prenatal testing is performed on placental biopsy through chorionic villus sampling (CVS) within 11 – 12 weeks of gestation or amniocentesis within 15 – 17 weeks of gestation. CVS is the preferred method as it provides higher DNA quality and greater safety for the pregnancy. The obtained DNA from placental biopsy can be analyzed through NGS or CNV detection. For non-invasive prenatal diagnostic options, relative haplotype dosage analysis (RHDO) may be performed. “RHDO analysis examines SNPs in the cell-free DNA from a maternal blood sample and shows whether the male foetus has inherited the high risk or low risk haplotype across the DMD gene” (Fratter et al., 2020).
References
- AAN. (2018). Evidence-based guideline summary: evaluation, diagnosis, and management of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001783
- Aartsma-Rus, A., Hegde, M., Ben-Omran, T., Buccella, F., Ferlini, A., Gallano, P., Howell, R. R., Leturcq, F., Martin, A. S., Potulska-Chromik, A., Saute, J. A., Schmidt, W. M., Sejersen, T., Tuffery-Giraud, S., Uyguner, Z. O., Witcomb, L. A., Yau, S., & Nelson, S. F. (2019). Evidence-Based Consensus and Systematic Review on Reducing the Time to Diagnosis of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J Pediatr, 204, 305-313.e314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.10.043
- Abbs, S., Tuffery-Giraud, S., Bakker, E., Ferlini, A., Sejersen, T., & Mueller, C. R. (2010). Best practice guidelines on molecular diagnostics in Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophies. Neuromuscul Disord, 20(6), 422-427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2010.04.005
- Amberger, J. S., Bocchini, C. A., Schiettecatte, F., Scott, A. F., & Hamosh, A. (2014). OMIM.org: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®), an online catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Research, 43(D1), D789-D798. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1205
- Arbustini, E., Di Toro, A., Giuliani, L., Favalli, V., Narula, N., & Grasso, M. (2018). Cardiac Phenotypes in Hereditary Muscle Disorders: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol, 72(20), 2485-2506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2018.08.2182
- Birnkrant, D. J., Bushby, K., Bann, C. M., Apkon, S. D., Blackwell, A., Brumbaugh, D., Case, L. E., Clemens, P. R., Hadjiyannakis, S., Pandya, S., Street, N., Tomezsko, J., Wagner, K. R., Ward, L. M., & Weber, D. R. (2018). Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 1: diagnosis, and neuromuscular, rehabilitation, endocrine, and gastrointestinal and nutritional management. Lancet Neurol, 17(3), 251-267. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(18)30024-3
- Brandsema, J. F., & Darras, B. T. (2015). Dystrophinopathies. Semin Neurol, 35(04), 369-384. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1558982
- Bushby, K., Finkel, R., Birnkrant, D. J., Case, L. E., Clemens, P. R., Cripe, L., Kaul, A., Kinnett, K., McDonald, C., Pandya, S., Poysky, J., Shapiro, F., Tomezsko, J., & Constantin, C. (2010). Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 1: diagnosis, and pharmacological and psychosocial management. Lancet Neurol, 9(1), 77-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(09)70271-6
- Chamberlain, J. S., Chamberlain, J. R., Fenwick, R. G., Ward, P. A., Caskey, C. T., Dimnik, L. S., Bech-Hansen, N. T., Hoar, D. I., Richards, S., Covone, A. E., Govanni, R., Abbs, S., Bentley, D. R., Bobrow, M., Rysiecki, G., Ray, P. N., Boileau, C., Junien, C., Boehm, C., . . . Rysiecki, G. (1992). Diagnosis of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies by polymerase chain reaction. A multicenter study. JAMA, 267(19), 2609-2615. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1992.03480190051030
- Dai, Y., Li, P., Wang, Z., Liang, F., Yang, F., Fang, L., Huang, Y., Huang, S., Zhou, J., Wang, D., Cui, L., & Wang, K. (2020). Single-molecule optical mapping enables quantitative measurement of D4Z4 repeats in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD). Journal of Medical Genetics, 57(2), 109. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2019-106078
- Darras, B. T. (2024a, 09/30/2024). Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy: Clinical features and diagnosis. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/duchenne-and-becker-muscular-dystrophy-clinical-features-and-diagnosis
- Darras, B. T. (2024b, March 20, 2024). Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/emery-dreifuss-muscular-dystrophy
- Darras, B. T. (2024c, 01/19/2024). Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/facioscapulohumeral-muscular-dystrophy
- Darras, B. T. (2024d, 02/01/2024). Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/limb-girdle-muscular-dystrophy
- Darras, B. T. (2024e, July 12, 2024). Oculopharyngeal, distal and congenital muscular dystrophies. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/oculopharyngeal-distal-and-congenital-muscular-dystrophies
- Darras, B. T., Urion, D. K., & Ghosh, P. S. (2000, 01/20/2022). Dystrophinopathies. University of Washington, Seattle. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1119/
- de Greef, J. C., Lemmers, R. J., Camano, P., Day, J. W., Sacconi, S., Dunand, M., van Engelen, B. G., Kiuru-Enari, S., Padberg, G. W., Rosa, A. L., Desnuelle, C., Spuler, S., Tarnopolsky, M., Venance, S. L., Frants, R. R., van der Maarel, S. M., & Tawil, R. (2010). Clinical features of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy 2. Neurology, 75(17), 1548-1554. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f96175
- Ebert, S. E., Meiling, J. B., Caress, J. B., Gandhi Mehta, R. K., Baute Penry, V., Puwanant, A., & Cartwright, M. S. (2024). Clinical Utility and Diagnostic Yield of Genetic Testing for
- Inherited Neuromuscular Disorders in a Single, Large Neuromuscular Center. Neurology Clinical Practice, 14(2), e200268. https://doi.org/doi:10.1212/CPJ.0000000000200268
- Fanin, M., Nascimbeni, A. C., Aurino, S., Tasca, E., Pegoraro, E., Nigro, V., & Angelini, C. (2009). Frequency of LGMD gene mutations in Italian patients with distinct clinical phenotypes. Neurology, 72(16), 1432-1435. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a1885e
- Fratter, C., Dalgleish, R., Allen, S. K., Santos, R., Abbs, S., Tuffery-Giraud, S., & Ferlini, A. (2020). EMQN best practice guidelines for genetic testing in dystrophinopathies. European Journal of Human Genetics, 28(9), 1141-1159. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41431-020-0643-7
- Ghaoui, R., Cooper, S. T., Lek, M., Jones, K., Corbett, A., Reddel, S. W., Needham, M., Liang, C., Waddell, L. B., Nicholson, G., O'Grady, G., Kaur, S., Ong, R., Davis, M., Sue, C. M., Laing, N. G., North, K. N., MacArthur, D. G., & Clarke, N. F. (2015). Use of Whole-Exome Sequencing for Diagnosis of Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophy: Outcomes and Lessons Learned. JAMA Neurol, 72(12), 1424-1432. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.2274
- Hamanaka, K., Sikrova, D., Mitsuhashi, S., Masuda, H., Sekiguchi, Y., Sugiyama, A., Shibuya, K., Lemmers, R., Goossens, R., Ogawa, M., Nagao, K., Obuse, C., Noguchi, S., Hayashi, Y. K., Kuwabara, S., Balog, J., Nishino, I., & van der Maarel, S. M. (2020). Homozygous nonsense variant in LRIF1 associated with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Neurology, 94(23), e2441-e2447. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000009617
- Hamel, J., & Tawil, R. (2018). Facioscapulohumeral Muscular Dystrophy: Update on Pathogenesis and Future Treatments. Neurotherapeutics, 15(4), 863-871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-018-00675-3
- Han, S., Xu, H., Zheng, J., Sun, J., Feng, X., Wang, Y., Ye, W., Ke, Q., Ren, Y., Yao, S., Zhang, S., Chen, J., Griggs, R. C., Zhao, Z., Qi, M., & Gatheridge, M. A. (2020). Population-Wide Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Carrier Detection by CK and Molecular Testing. BioMed Research International, 2020, 8396429. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8396429
- Harris, E., Topf, A., Barresi, R., Hudson, J., Powell, H., Tellez, J., Hicks, D., Porter, A., Bertoli, M., Evangelista, T., Marini-Betollo, C., Magnusson, O., Lek, M., MacArthur, D., Bushby, K., Lochmuller, H., & Straub, V. (2017). Exome sequences versus sequential gene testing in the UK highly specialised Service for Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 12(1), 151. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-017-0699-9
- Haynes, P., Bomsztyk, K., & Miller, D. G. (2018). Sporadic DUX4 expression in FSHD myocytes is associated with incomplete repression by the PRC2 complex and gain of H3K9 acetylation on the contracted D4Z4 allele. Epigenetics Chromatin, 11(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13072-018-0215-z
- Kang, P. B., Morrison, L., Iannaccone, S. T., Graham, R. J., Bonnemann, C. G., Rutkowski, A., Hornyak, J., Wang, C. H., North, K., Oskoui, M., Getchius, T. S., Cox, J. A., Hagen, E. E., Gronseth, G., & Griggs, R. C. (2015). Evidence-based guideline summary: evaluation, diagnosis, and management of congenital muscular dystrophy: Report of the Guideline Development Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Issues Review Panel of the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine. Neurology, 84(13), 1369-1378. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000001416
- Kim, E. Y., Lee, J. W., Suh, M. R., Choi, W. A., Kang, S. W., & Oh, H. J. (2017). Correlation of Serum Creatine Kinase Level With Pulmonary Function in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Ann Rehabil Med, 41(2), 306-312. https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2017.41.2.306
- Lemmers, R. J., Osborn, M., Haaf, T., Rogers, M., Frants, R. R., Padberg, G. W., Cooper, D. N., van der Maarel, S. M., & Upadhyaya, M. (2003). D4F104S1 deletion in facioscapulohumeral
- muscular dystrophy: phenotype, size, and detection. Neurology, 61(2), 178-183. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000078889.51444.81
- Lemmers, R. J., Tawil, R., Petek, L. M., Balog, J., Block, G. J., Santen, G. W., Amell, A. M., van der Vliet, P. J., Almomani, R., Straasheijm, K. R., Krom, Y. D., Klooster, R., Sun, Y., den Dunnen, J. T., Helmer, Q., Donlin-Smith, C. M., Padberg, G. W., van Engelen, B. G., de Greef, J. C., . . . van der Maarel, S. M. (2012). Digenic inheritance of an SMCHD1 mutation and an FSHD-permissive D4Z4 allele causes facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy type 2. Nat Genet, 44(12), 1370-1374. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2454
- Lemmers, R. J. L. F., O’Shea, S., Padberg, G. W., Lunt, P. W., & van der Maarel, S. M. (2012). Best practice guidelines on genetic diagnostics of Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy: Workshop 9th June 2010, LUMC, Leiden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscular Disorders, 22(5), 463-470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2011.09.004
- Luce, L. N., Dalamon, V., Ferrer, M., Parma, D., Szijan, I., & Giliberto, F. (2016). MLPA analysis of an Argentine cohort of patients with dystrophinopathy: Association of intron breakpoints hot spots with STR abundance in DMD gene. J Neurol Sci, 365, 22-30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2016.03.047
- Monies, D., Alhindi, H. N., Almuhaizea, M. A., Abouelhoda, M., Alazami, A. M., Goljan, E., Alyounes, B., Jaroudi, D., AlIssa, A., Alabdulrahman, K., Subhani, S., El-Kalioby, M., Faquih, T., Wakil, S. M., Altassan, N. A., Meyer, B. F., & Bohlega, S. (2016). A first-line diagnostic assay for limb-girdle muscular dystrophy and other myopathies. Hum Genomics, 10(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40246-016-0089-8
- Mul, K., Voermans, N. C., Lemmers, R., Jonker, M. A., van der Vliet, P. J., Padberg, G. W., van Engelen, B. G. M., van der Maarel, S. M., & Horlings, C. G. C. (2018). Phenotype-genotype relations in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy type 1. Clin Genet. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.13446
- Murphy, A. P., & Straub, V. (2015). The Classification, Natural History and Treatment of the Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophies. J Neuromuscul Dis, 2(s2), S7-s19. https://doi.org/10.3233/jnd-150105
- Murugan, S., Chandramohan, A., & Lakshmi, B. R. (2010). Use of multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene mutation analysis. Indian J Med Res, 132, 303-311. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/46288551_Use_of_multiplex_ligation-dependent_probe_amplification_MLPA_for_Duchenne_muscular_dystrophy_DMD_gene_mutation_analysis
- Nallamilli, B. R. R., Chakravorty, S., Kesari, A., Tanner, A., Ankala, A., Schneider, T., da Silva, C., Beadling, R., Alexander, J. J., Askree, S. H., Whitt, Z., Bean, L., Collins, C., Khadilkar, S., Gaitonde, P., Dastur, R., Wicklund, M., Mozaffar, T., Harms, M., . . . Hegde, M. (2018). Genetic landscape and novel disease mechanisms from a large LGMD cohort of 4656 patients. Ann Clin Transl Neurol, 5(12), 1574-1587. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.649
- Narayanaswami, P., Weiss, M., Selcen, D., David, W., Raynor, E., Carter, G., Wicklund, M., Barohn, R. J., Ensrud, E., Griggs, R. C., Gronseth, G., & Amato, A. A. (2014). Evidence-based guideline summary: diagnosis and treatment of limb-girdle and distal dystrophies: report of the guideline development subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the practice issues review panel of the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine. Neurology, 83(16), 1453-1463. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000000892
- Norwood, F., de Visser, M., Eymard, B., Lochmuller, H., & Bushby, K. (2007). EFNS guideline on diagnosis and management of limb girdle muscular dystrophies. Eur J Neurol, 14(12), 1305-1312. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2007.01979.x
- O'Grady, G. L., Lek, M., Lamande, S. R., Waddell, L., Oates, E. C., Punetha, J., Ghaoui, R., Sandaradura, S. A., Best, H., Kaur, S., Davis, M., Laing, N. G., Muntoni, F., Hoffman, E., MacArthur, D. G., Clarke, N. F., Cooper, S., & North, K. (2016). Diagnosis and etiology of congenital muscular dystrophy: We are halfway there. Annals of Neurology, 80(1), 101-111. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ana.24687
- Ozyilmaz, B., Kirbiyik, O., Ozdemir, T. R., Kaya Ozer, O., Kutbay, Y. B., Erdogan, K. M., Guvenc, M. S., Kale, M. Y., Gazeteci, H., Kilic, B., Sertpoyraz, F., Diniz, G., Baydan, F., Gencpinar, P., Dundar, N. O., & Yis, U. (2019). Impact of next-generation sequencing panels in the evaluation of limb-girdle muscular dystrophies. Ann Hum Genet, 83(5), 331-347. https://doi.org/10.1111/ahg.12319
- Petek, L. M., Rickard, A. M., Budech, C., Poliachik, S. L., Shaw, D., Ferguson, M. R., Tawil, R., Friedman, S. D., & Miller, D. G. (2016). A cross sectional study of two independent cohorts identifies serum biomarkers for facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD). Neuromuscul Disord, 26(7), 405-413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2016.04.012
- Reddy, H. M., Cho, K. A., Lek, M., Estrella, E., Valkanas, E., Jones, M. D., Mitsuhashi, S., Darras, B. T., Amato, A. A., Lidov, H. G., Brownstein, C. A., Margulies, D. M., Yu, T. W., Salih, M. A., Kunkel, L. M., MacArthur, D. G., & Kang, P. B. (2017). The sensitivity of exome sequencing in identifying pathogenic mutations for LGMD in the United States. J Hum Genet, 62(2), 243-252. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2016.116
- Romitti, P. A., Zhu, Y., Puzhankara, S., James, K. A., Nabukera, S. K., Zamba, G. K., Ciafaloni, E., Cunniff, C., Druschel, C. M., Mathews, K. D., Matthews, D. J., Meaney, F. J., Andrews, J. G., Conway, K. M., Fox, D. J., Street, N., Adams, M. M., Bolen, J., & STARnet, M. D. (2015). Prevalence of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies in the United States. Pediatrics, 135(3), 513-521. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2014-2044
- Rosenberg, A., Tian, C., He, H., Ulm, E., Collins Ruff, K., & B. Nagaraj, C. (2023). An evaluation of clinical presentation and genetic testing approaches for patients with neuromuscular disorders. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 191(11), 2679-2692. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/ajmg.a.63356
- Scionti, I., Greco, F., Ricci, G., Govi, M., Arashiro, P., Vercelli, L., Berardinelli, A., Angelini, C., Antonini, G., Cao, M., Di Muzio, A., Moggio, M., Morandi, L., Ricci, E., Rodolico, C., Ruggiero, L., Santoro, L., Siciliano, G., Tomelleri, G., . . . Tupler, R. (2012). Large-scale population analysis challenges the current criteria for the molecular diagnosis of fascioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet, 90(4), 628-635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.02.019
- Straub, V., Murphy, A., Udd, B., & group, L. w. s. (2018). 229th ENMC international workshop: Limb girdle muscular dystrophies - Nomenclature and reformed classification Naarden, the Netherlands, 17-19 March 2017. Neuromuscul Disord, 28(8), 702-710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmd.2018.05.007
- Tawil, R., Kissel, J. T., Heatwole, C., Pandya, S., Gronseth, G., & Benatar, M. (2015). Evidence-based guideline summary: Evaluation, diagnosis, and management of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Issues Review Panel of the American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine. Neurology, 85(4), 357-364. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000001783
- van den Boogaard, M. L., Lemmers, R., Balog, J., Wohlgemuth, M., Auranen, M., Mitsuhashi, S., van der Vliet, P. J., Straasheijm, K. R., van den Akker, R. F. P., Kriek, M., Laurense-Bik, M. E. Y., Raz, V., van Ostaijen-Ten Dam, M. M., Hansson, K. B. M., van der Kooi, E. L., Kiuru-Enari, S., Udd, B., van Tol, M. J. D., Nishino, I., . . . van der Maarel, S. M. (2016). Mutations in DNMT3B Modify Epigenetic Repression of the D4Z4 Repeat and the Penetrance of Facioscapulohumeral Dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet, 98(5), 1020-1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.03.013
- van der Maarel, S. M., Tawil, R., & Tapscott, S. J. (2011). Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy and DUX4: breaking the silence. Trends Mol Med, 17(5), 252-258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2011.01.001
- Vengalil, S., Preethish-Kumar, V., Polavarapu, K., Mahadevappa, M., Sekar, D., Purushottam, M., Thomas, P. T., Nashi, S., & Nalini, A. (2017). Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Becker Muscular Dystrophy Confirmed by Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification: Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in a Large Cohort. J Clin Neurol, 13(1), 91-97. https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2017.13.1.91
- Wang, C. H., Bonnemann, C. G., Rutkowski, A., Sejersen, T., Bellini, J., Battista, V., Florence, J. M., Schara, U., Schuler, P. M., Wahbi, K., Aloysius, A., Bash, R. O., Beroud, C., Bertini, E., Bushby, K., Cohn, R. D., Connolly, A. M., Deconinck, N., Desguerre, I., . . . Zeller, R. (2010). Consensus statement on standard of care for congenital muscular dystrophies. J Child Neurol, 25(12), 1559-1581. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073810381924
- Wang, H., Xu, Y., Liu, X., Wang, L., Jiang, W., Xiao, B., Wei, W., Chen, Y., Ye, W., & Ji, X. (2017). Prenatal diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in 131 Chinese families with dystrophinopathy. Prenat Diagn, 37(4), 356-364. https://doi.org/10.1002/pd.5019
- Wicklund, M. P. (2019). The Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophies. Continuum (Minneap Minn), 25(6), 1599-1618. https://doi.org/10.1212/CON.0000000000000809
- Wicklund, M. P., & Kissel, J. T. (2014). The limb-girdle muscular dystrophies. Neurol Clin, 32(3), 729-749, ix. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2014.04.005
- Yang, J., Li, S. Y., Li, Y. Q., Cao, J. Q., Feng, S. W., Wang, Y. Y., Zhan, Y. X., Yu, C. S., Chen, F., Li, J., Sun, X. F., & Zhang, C. (2013). MLPA-based genotype-phenotype analysis in 1053 Chinese patients with DMD/BMD. BMC Med Genet, 14, 29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-14-29
- Zhang, T., Liu, S., Wei, T., Yong, J., Mao, Y., Lu, X., Xie, J., Ke, Q., Jin, F., & Qi, M. (2013). Development of a comprehensive real-time PCR assay for dystrophin gene analysis and prenatal diagnosis of Chinese families. Clin Chim Acta, 424, 33-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2013.05.006
Coding Section
| Code | Number |
Description |
| CPT | 81161 |
DMD (dystrophin) (e.g., Duchenne/Beckerduchenne/becker muscular dystrophy) deletion analysis, and duplication analysis, if performed |
| 81187 |
CNBP (CCHC-type zinc finger nucleic acid binding protein) (e.g., myotonic dystrophy type 2) gene analysis, evaluation to detect abnormal (e.g., expanded) alleles |
|
| 81234 |
DMPK (DM1 protein kinase) (e.g., myotonic dystrophy type 1) gene analysis; evaluation to detect abnormal (expanded) alleles |
|
| 81239 |
DMPK (DM1 protein kinase) (e.g., myotonic dystrophy type 1) gene analysis; characterization of alleles (e.g., expanded size) |
|
| 81312 |
PABPN1 (poly[A] binding protein nuclear 1) (e.g., oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy) gene analysis, evaluation to detect abnormal (e.g., expanded) alleles |
|
| 81400 |
Molecular pathology procedure, Level 1 (e.g., identification of single germline variant [e.g., SNP] by techniques such as restriction enzyme digestion or melt curve analysis) |
|
| 81404 |
Molecular pathology procedure, Level 5 (e.g., analysis of 2 – 5 exons by DNA sequence analysis, mutation scanning or duplication/deletion variants of 6 – 10 exons, or characterization of a dynamic mutation disorder/triplet repeat by Southern blot analysis) |
|
| 81405 |
Molecular pathology procedure, Level 6 (e.g., analysis of 6 – 10 exons by DNA sequence analysis, mutation scanning or duplication/deletion variants of 11 – 25 exons, regionally targeted cytogenomic array analysis) |
|
| 81406 |
Molecular pathology procedure, Level 7 (e.g., analysis of 11-25 exons by DNA sequence analysis, mutation scanning or duplication/deletion variants of 26 – 50 exons, cytogenomic array analysis for neoplasia) |
|
| 81408 |
Molecular pathology procedure, Level 9 (e.g., analysis of > 50 exons in a single gene by DNA sequence analysis) |
|
| 81479 |
Unlisted molecular pathology procedure |
|
| 0218U |
Neurology (muscular dystrophy), DMD gene sequence analysis, including small sequence changes, deletions, duplications, and variants in non-uniquely mappable regions, blood or saliva, identification and characterization of genetic variants |
|
| S3853 |
Genetic testing for myotonic muscular dystrophy |
Procedure and diagnosis codes on Medical Policy documents are included only as a general reference tool for each policy. They may not be all-inclusive.
This medical policy was developed through consideration of peer-reviewed medical literature generally recognized by the relevant medical community, U.S. FDA approval status, nationally accepted standards of medical practice and accepted standards of medical practice in this community, and other nonaffiliated technology evaluation centers, reference to federal regulations, other plan medical policies and accredited national guidelines.
"Current Procedural Terminology © American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved"
History From 2018 Forward